
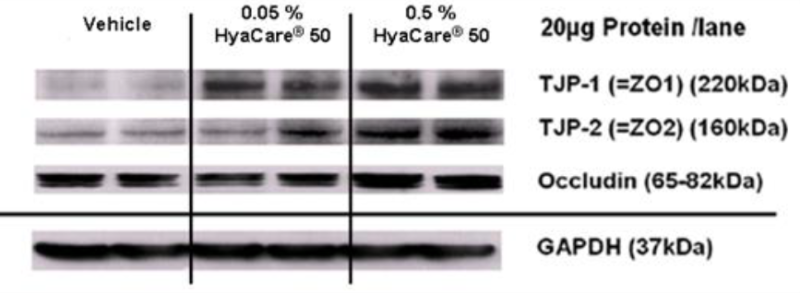
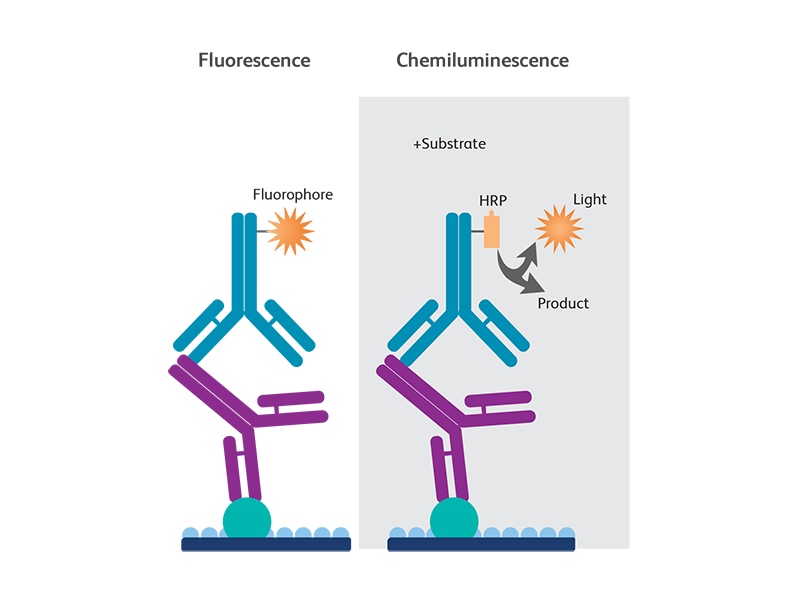
Determine the Appropriate Reference Signal for Data Normalization.Determine the Linear Dynamic Range of Protein Loading.Careful Experimental Design Produces Reliable and Reproducible Data.e., untreated)Amount per mass of drug or compoundPreservation method and time. e., normal)Technical (same sample per well)Times of embryonic developmentSample extraction methodPotential internal controlsUntreated versus drug treated (i. )Biological (difft sample per well)Growth conditions (media and time or OD)Precise time for you to harvest cells or tissuesTarget proteins implicatedNormal versus disease (i. We have recently published an updated approach to produce quantitative densitometric data from western blots (Taylor et al., 2022) and here we summarize the complete western blot workflow with a focus on sample preparation and data analysis for quantitative western blotting. The calculations are based on the differential densitometry of the associated chemiluminescent and/or fluorescent signals from the blots and this now requires a fundamental shift in the experimental methodology, acquisition, and interpretation of the data. In the past, western blotting was used simply to detect a specific target protein in a complex mixture, but now journal editors and reviewers are requesting the quantitative interpretation of western blot data in terms of fold changes in protein expression between samples. Although there have been significant advances in both the imaging and reagent technologies to improve sensitivity, dynamic range of detection, and the applicability of multiplexed target detection, the basic technique has remained essentially unchanged. Western blotting is a technique that has been in practice for more than three decades that began as a means of detecting a protein target in a complex sample. The Design of a Quantitative Western Blot Experiment
#Immunoblotting vs western blot how to
How western blots work, and how to read them in a scientific journal article. Video advice: Introduction to western blots part 2 Often the membrane is cut into strips to facilitate testing of a large number of samples for antibodies directed against the blotted protein (antigen). All sites on the membrane which do not contain blotted protein from the gel can then be non-specifically “blocked” so that antibody (serum) will not non-specifically bind to them, causing a false positive result. For this procedure, an electric current is applied to the gel so that the separated proteins transfer through the gel and onto the membrane in the same pattern as they separate on the SDS-PAGE. Sufficiently separated proteins in an SDS-PAGE can be transferred to a solid membrane for WB analysis.
#Immunoblotting vs western blot free
Finally after excess second antibody is washed free of the blot, a substrate is added which will precipitate upon reaction with the conjugate resulting in a visible band where the primary antibody bound to the protein. This anti-Ig-enzyme is commonly called a “second antibody” or “conjugate”. goat anti-human IgG- alkaline phosphatase). In order to detect the antibodies which have bound, anti-immunoglobulin antibodies coupled to a reporter group such as the enzyme alkaline phosphatase are added (e.g. If there are any antibodies present which are directed against one or more of the blotted antigens, those antibodies will bind to the protein(s) while other antibodies will be washed away at the end of the incubation. To detect the antigen blotted on the membrane, a primary antibody (serum) is added at an appropriate dilution and incubated with the membrane.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
